Navigation: Previous Page | Contents | Next Page
Appendix 5
Legislative tools for combating serious and organised
crime – Australian jurisdictions
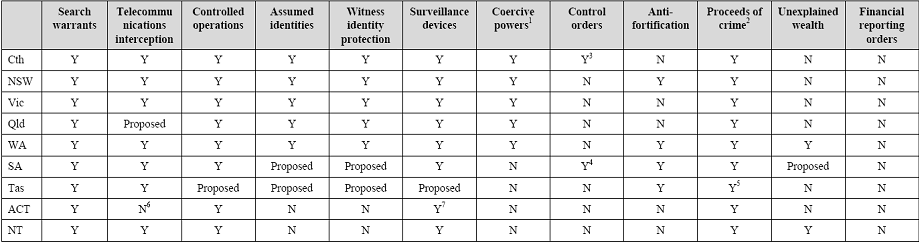
Source: Attorney-General's Department, answer to question on
notice, 6 November 2008 (received 23 December 2008), Appendix A.
1 Coercive powers are contained in the Australian Crime Commission Act 2002 and the mirror ACC legislation of the States and Territories. Additionally, legislation in NSW, Victoria, Queensland and WA gives certain state agencies coercive powers in relation to serious organised crime.
2 There are provisions in WA and NT (and proposed in SA) allowing for more severe recovery action to be taken where a person has been declared a drug trafficker on the basis of certain conditions (e.g. a number of convictions for drug offences, or being convicted of a certain category of drug offence). For example, in WA all property of a declared drug trafficker may be forfeited regardless of whether it is the proceeds of crime.
3 A person can be subject to a control order if the order substantially assists in preventing a terrorist attach or if the person has trained with a terrorist organisation.
4 Control orders can be issued against members of 'declared organisation', former members of such organisations and others who engage in serious criminal activity. The Attorney-General can make a declaration about an organisation if satisfied that the members of the organisation associate for the purpose of organising, planing, supporting, facilitating or engaging in serious criminal activity and the organisation represents a risk to public safety and order in SA.
5 There are no civil confiscation provisions in Tasmania.
6 There is no ACT specific legislation. The Commonwealth legislation applies in the ACT to offences committed against the Commonwealth.
7 Listening devices only. The Commonwealth legislation applies in the ACT to offences committed against the Commonwealth. Navigation: Previous Page | Contents | Next Page
Top
|