Introductory Info
Date introduced: 25 August 2021
House: House of Representatives
Portfolio: Indigenous Australians
Commencement: See details under the subheading ‘Commencement details’ in this Digest.
The Bills Digest at a glance
The Aboriginal
Land Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Economic Empowerment) Bill 2021
(the Bill) makes significant and far-reaching reforms to the Aboriginal Land
Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (the Act). The Bill contains four
Schedules, of which the amendments made in the first Schedule are the most
significant.
Schedule 1’s amendments create a Northern Territory
Aboriginal Investment Corporation (NTAIC), lay out the procedure for electing
and appointing its board and guiding its investments, and put in place
transitional arrangements. Approximately half ($680 million) of the current
accumulated balance of the Aboriginals Benefit Account (ABA) ($1.3 billion)
will be transferred to the NTAIC over three years. This will allow the
transferred funds to potentially achieve much greater results than management
under the conservative requirements of the Public Governance, Performance
and Accountability Act 2013 (PGPA Act) for investment of special
accounts, although the NTAIC must attend to several, potentially conflicting
investment goals. The NTAIC will be managed by a board with a majority elected
by the Aboriginal Land Councils of the Northern Territory, and its investments
will be actively directed towards Indigenous economic development. The
remaining balance and ongoing operation of the ABA will still be controlled by
the Minister for Indigenous Australians. The Bill abolishes the Advisory
Council which currently advises the Minister on ABA spending.
Schedule 2 implements several amendments recommended by
the Aboriginal Land Commissioner’s 2013 Review of Part IV of the Aboriginal
Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 concerning mining activity under
the Act.[1]
These amendments update the Act to reflect Northern Territory legislation and
developments in mining (for example, concerning geothermal energy), clarify and
change aspects of the approval process (including meeting requirements with
Traditional Owners), clarify the process for dealing with relatively low impact
mining for ‘extractive minerals’ (clay, gravel, sand, et cetera), and change
parts of the ministerial approval process by removing delegation of some
Commonwealth ministerial approvals from the Northern Territory mining minister
and removing the requirement for Commonwealth ministerial approval for some
mining projects.
Schedule 3 makes changes to land administration and
control processes including those for township leases, delegation of land
council functions, land in escrow, ministerial approvals, and control over
access to Aboriginal land. These alter contentious amendments first made in
2006 and 2007 by the Howard Government. These changes act on long-standing Land
Council concerns.
Schedule 4 aligns the statutory requirements for payments
into and out of the ABA with current practice, reflecting that payments are
currently made based on estimates of mining royalties rather than final
figures, meaning that overpayments may need to be recouped or underpayments
supplemented when final figures become available.
This Bill offers a Solomonic resolution to the Aboriginal
Land Councils’ long-standing (particularly since 2006) concerns about the use
of the Aboriginals Benefit Account by the Commonwealth Government, by dividing
the account’s accumulated balance in half. One half will now be invested
through the NTAIC, while the Commonwealth will arguably increase its
expenditure powers (and maintain the current investment strategy) over the
other half. The Land Councils have expressed satisfaction with this compromise.
Purpose and Structure of the
Bill
The purpose of the Aboriginal
Land Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Economic Empowerment) Bill 2021
(the Bill) is to amend the Aboriginal Land
Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (the Act) in four areas, covered
by four Schedules:
-
Schedule 1 will establish the Northern Territory
Aboriginal Investment Corporation (NTAIC) as a new Aboriginal-controlled corporate
Commonwealth entity to strategically invest in Aboriginal businesses and
commercial projects and make other payments to or for the benefit of Aboriginal
peoples in the NT
-
Schedule 2 will amend the exploration and mining
provisions of the Act in order to clarify and streamline a number of approval
processes
-
Schedule 3 will amend and clarify land administration
provisions, including on township leases, access to Aboriginal land, land under
escrow and other matters
-
Schedule 4 will align payments from the Aboriginals
Benefit Account (ABA) with the Commonwealth’s financial framework and the
timing of mineral royalties payments from the Northern Territory (NT).[2]
Commencement details
The substantive amendments relating to the NTAIC contained
in Part 1 of Schedule 1 commence on Proclamation or 12 months
after Royal Assent, whichever is sooner. The majority of the remaining
amendments commence on the day after Royal Assent, which the exception of
amendments relating to township land and increases to penalties for entering or
remaining on Aboriginal land (Part 4 of Schedule 3) which commence 12
months after Royal Assent.
Background
The Act sets out a scheme for the claiming, granting,
control and management of Aboriginal land by traditional Aboriginal owners in
the NT. The Fraser Government passed the Act after the dismissal of the Whitlam
Government meant the original Aboriginal Land (Northern Territory) Bill 1975
lapsed.[3]
Fraser’s Act and Whitlam’s Bill both responded to Justice Woodward’s 1973–1974
Aboriginal Land Rights Commission report,[4]
which was accepted in principle by both major parties.[5] While there were some
significant differences between the two pieces of legislation, the Act
ultimately passed with bipartisan support.[6]
The Act provides for title to land to be granted to a Land
Trust on behalf of the traditional owners.[7]
Title is inalienable and equivalent to freehold title but is held communally,
reflecting the nature of Aboriginal land ownership. The Act also provides for
Land Councils, who represent traditional owners and negotiate with mining
proponents and land developers on their behalf.[8]
It provides that royalty equivalent payments from mining on Aboriginal land are
paid into an Aboriginals Benefit Account (ABA).[9]
The ABA funds Land Councils, compensatory payments to traditional owners, and
grants after payment of a Mining Withholding Tax (MWT) (introduced in 1979).[10] The ABA itself
predates the Act, being originally enacted as a beneficial trust fund by then
Minister for Territories Paul Hasluck in 1952, as reparation for allowing
mining on what were then Aboriginal reserves.[11]
The Explanatory Memorandum to the Bill states:
… [a]mendments to the Land Rights Act are not common.
Aboriginal stakeholders in the NT have strong voices through their Land
Councils (the NLC [Northern Land Council], CLC [Central Land Council], ALC
[Anindilyakwa Land Council] and TLC [Tiwi Land Council]) and the Commonwealth
has committed to only amend the Land Rights Act with their support.[12]
Despite this statement, the Act has been amended many
times – sometimes simply to add additional land claims, which may require
parliamentary action,[13]
but frequently for more fundamental amendments. On many occasions (particularly
in 2006 and 2007, see below) it has been amended in ways which the Land
Councils have not supported. Many key features of the Bill are best understood
as rollbacks of, or compromises over, past amendments to which the Land
Councils objected at the time. Other proposed amendments are the results of
reviews of the Act which have not been acted upon to date.
Past amendments, reports and reviews
Past amendments, policies, reports and reviews to which
this Bill directly or indirectly responds include:
-
the 1984 Report on the Review of the Aboriginals Benefit Trust
Account (and related financial matters) in the Northern Territory land rights
legislation by Professor Jon Altman,[14]
which recommended, among other matters, that, over time, some functions of the
ABA should be transitioned to a statutory body with its grant-making function
controlled by an Aboriginal board, and the range of permitted investments of
the ABA’s balance should be widened. This original recommendation is alluded to
in the NIAA’s fact sheet on the proposed NTAIC.[15]
-
the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment Act
(No 3) 1987,[16]
which, among other matters, mandated conjoined applications for exploration and
mining in Aboriginal land (that is, consent to an exploration licence also
acted as consent for a mining licence) and other changes to the mining approval
process.[17]
-
ANAO Report 22 of 2002–03, Northern Territory Land Councils
and the Aboriginals Benefit Account,[18]
and the 2008 Department of Finance and Deregulation, Office of Evaluation and
Audit (Indigenous Programs) report Performance Audit of the Aboriginals
Benefit Account (the OEA report)[19]
both recommended, among other matters, that the managing entity (in 2002 this
was the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission (ATSIC) and in 2008
this was the Department of Families, Housing, Community Services and Indigenous
Affairs (FaHCSIA)) pursue a more active investment strategy for the funds
accumulated in the ABA.[20]
At the time the OEA report was critical of FaHSCIA’s
administration of payments under section 64(4) of the Act, finding that
FaHSCIA’s assessment of grant applications was ‘cursory’ and that the
Aboriginals Benefit Account Advisory Committee (ABAAC) was not provided with
sufficient information by the Department to enable it to effectively contribute
to decisions.[21]
Neither recommendation for more active investment management was acted upon, in
part because of the difficulty of reconciling an investment strategy with the
requirements of the Financial Management and Accountability Act 1997 (the
precursor to the current PGPA Act).[22]
-
the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission Amendment
Act 2005,[23]
which abolished ATSIC. ATSIC had been the lead agency administering the ABA.
After its abolition, Ministers, through the relevant department, took a more
active role in managing the ABA.
-
the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment Act
2006 (the 2006 Amendments),[24]
among other matters:
- created the legislative structure for township leasing by an
entity (since administered by the Commonwealth’s Executive Director of Township
Leasing (EDTL) under Part IIA of the Act, which was inserted by the Aboriginal Land
Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Township Leasing) Act 2007)
- provided for township leasing expenses and leases to be paid out
of the ABA (rather than the leasee, for example, the NT or Commonwealth
governments)
- enabled Land Councils to delegate some of their functions to
corporations formed under the Corporations
(Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander) Act 2006 (CATSI corporations)
-
changed a number of sections relating to mining approvals
processes in Part IV of the Act,
-
enabled the Minister to designate an amount of the ABA to be
retained and invested rather than distributed (the ‘investment amount’, section
62A)
- changed Land Councils’ income from the ABA from a statutory 40
per cent of mining royalty equivalents (potentially plus additional funds, see
below) to an amount determined by the Minister upon receiving budget estimates
prepared by the Land Councils
- removed the ability for the Minister to direct that additional
funds from the ABA be directed to Land Councils to meet their administrative
costs (former subsection 64(8) of the Act, instead such amounts would fall
under the broader amount determined by the Minister mentioned above)
- enabled the Minister to appoint some members of the ABAAC
(formerly a body entirely composed of Land Council appointees, with the
exception of the Chair) and
-
provided for a review of the amendments to Part IV (mining) to be
carried out five years after the amendments had commenced.
Several of these provisions, particularly those which paid
what would otherwise be normal government budget expenses (rent of land and
buildings) out of the ABA, and made Land Council budgets significantly more
dependent on ministerial approval, were strongly objected to by Land Councils
and others at the time. For further details of the 2006 Amendments, see its
Explanatory Memorandum,[25]
Bills Digest[26]
and Senate Standing Committees on Community Affairs Legislation Committee
Inquiry Report.[27]
-
the Families, Community Services and Indigenous Affairs and
Other Legislation Amendment (Northern Territory National Emergency Response and
Other Measures) Act 2007,[28]
which inserted section 74AA into the Act, as part of a suite of measures (in
Schedule 4 of that Act) that significantly increased governmental and private
non-Aboriginal access to Aboriginal land.[29]
-
in 2012, then Minister for Families, Housing, Community Services,
and Indigenous Affairs, Jenny Macklin, commissioned the Aboriginal Land
Commissioner, JR Mansfield, to carry out the review of Part IV of the Act as
legislated in the 2006 Amendments. The resulting Report on review of Part IV
of the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 (the 2013
Review) was completed in March 2013 and subsequently tabled in Parliament.[30] According to the
Explanatory Memorandum, the recommendations have since been the subject of a
Working Group consisting of the Commonwealth, NT Government, and the Land
Councils, which also carried out further consultations with mining industry
peak bodies.[31]
Many provisions of Schedule 2 of the Bill implement or respond to
recommendations of that review.
-
in 2013, the incoming Coalition Government committed to
supporting the Act,[32]
and to ‘resolve outstanding Aboriginal land claims in the Northern Territory
and to work with Indigenous land owners to ensure their land rights deliver the
economic opportunities that should come from owning your own land.’[33]
Manifestations of this commitment include the successful
resolution of the long-standing Kenbi land claim[34] and resolved land claims in
Kakadu, Urapanga, Anthony Lagoon,[35]
and Ammaroo,[36]
although former Minister for Indigenous Affairs, Nigel Scullion, also refused
to act upon a number of significant outstanding claims.[37] After initial suspicion of
the ‘deliver economic opportunities’ part of the Coalition Government’s
commitment,[38]
the Land Councils appear to have arrived at a rapprochement with Minister Wyatt[39] and to have
embraced the economic development possibilities offered by this Bill through
the NTAIC.
-
In 2019–20, the Joint Standing Committee on Northern Australia
held an Inquiry into the Opportunities and Challenges of the Engagement of
Traditional Owners in the Economic Development of Northern Australia.[40] This Committee
heard evidence about the potential uses of the ABA to promote economic
development for traditional owners.[41]
The Inquiry, and consequently its report, have been suspended due to the
COVID-19 pandemic.
Committee consideration
On 21 October 2021, after being passed by the House of
Representatives, the Bill was referred by the Selection of Bills Committee to
the Senate Standing Committee on Finance and Public Administration (Legislation
Committee) for inquiry
and report by 25 November 2021.[42]
Senate
Standing Committee for the Scrutiny of Bills
The Senate Standing Committee for the Scrutiny of Bills
considered the Bill in Scrutiny Digest 15 of 2021.[43] The Committee raised concerns
about proposed provisions which create no-invalidity clauses, use delegated
legislation, non-reviewable instruments, some reports not being tabled in
Parliament, and standing appropriations in the Bill, and requested further
advice from the Minister on these proposed sections.
The Committee noted that proposed subsection 65BH(3)
(item 6 of Schedule 1 of the Bill) and proposed subsection
12D(7) (item 25 of Schedule 3 of the Bill) state that a
failure to follow the procedural requirements set out in the Bill (to seek
Ministerial approval of investments over $100 million, and to seek
traditional owner approval of agreements over land held in escrow) does not
invalidate the transaction or agreement concerned. The Committee expressed
concern that such ‘no invalidity’ clauses may impact on the practical efficacy
of judicial review.[44]
The Committee noted that a number of proposed subsections
allow significant matters regarding the financial conduct of the NTAIC on
loans, investments, borrowings and loan guarantees, to be varied by the ‘NTAIC
rules’, a delegated legislative instrument to be made by the Minister (under proposed
section 65JE at item 6 of Schedule 1 of the Bill). The
Committee expressed concern at the use of delegated legislation for significant
details and asked the Minister for more advice on whether this was necessary
and appropriate, and whether the Bill could be amended to include ‘at least high-level
guidance’ on these matters in the primary legislation.[45]
The Committee noted while that the strategic investment
plan of the NTAIC prepared under proposed section 65C is to be tabled in
parliament, it is not a legislative instrument and therefore not subject to
parliamentary oversight. The Committee asked for the Minister’s advice on
whether the plan could be made a legislative instrument.[46]
The Committee also noted that as part of the transitional
measures, the Minister may request the Board of the NTAIC to prepare a progress
report on the strategic investment plan (item 19 of Schedule 1).
While the Minister may publish such a report on the internet (subitem
19(4) of Schedule 1), they are under no obligation to do so. The
Committee asked for the Minister’s advice on whether the progress report could
be tabled in Parliament and also be required, rather than permitted, to be
published online.[47]
The Committee noted that many parts of the procedure for a
body becoming an approved entity to hold a township lease under proposed
section 3AA (item 4 of Schedule 3 of the Bill) will be made
by a legislative instrument. The Committee asked for the Minister’s advice on
why this was necessary and appropriate, and whether the legislation could be
amended to provide at least high-level guidance in the primary legislation.[48]
The Minister responded to the committee in a letter dated
29 September 2021, which was published
by the Committee, along with its
response to the Minister, on 21 October 2021. The Minister stated (in
summary) that:
-
no-invalidity clauses were necessary and appropriate to protect
the rights of, and provide business certainty to, entities transacting with the
NTAIC and stakeholders negotiating with Land Councils
-
details of the NTAIC’s business functions are to be administered
through legislative instruments in order to provide flexibility for the NTAIC
to address investment-related risks and other commercial matters in a timely
way
-
the Strategic Investment Plan is administrative rather than
legislative in nature and hence is not required to be an instrument, and making
it subject to Parliamentary approval would weaken Aboriginal peoples’ and
organisations’ right to self-determination
-
the progress reports on the Strategic Investment Plan are likely
to be largely operational in nature, may contain commercially sensitive
material, and will in any case be followed by tabled plans and reports and
-
the township lease approval process already contains a number of
conditions that must be satisfied before the Minister issues an instrument and,
given that the conditions pertaining to particular townships cannot be
predicted in advance, the additional flexibility granted by a legislative
instrument is warranted.[49]
In its response to the Minister, the Committee largely
reiterated its original concerns, requested some additions to the Explanatory
Memorandum to take account of information supplied by the Minister, and drew
the attention of the Senate as a whole to its concerns and the Minister’s
responses.[50]
The Committee also drew matters relating to legislative instruments (NTAIC
business rules and township leasing) to the attention of the Senate Standing
Committee for the Scrutiny of Delegated Legislation.[51]
It is worth noting that similar concerns about investment
plans by a Commonwealth corporation not being set out in a reviewable
legislative instrument were raised by the Committee with respect to the Investment
Mandate of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Land and Sea Future Fund.[52] Unlike the
NTAIC’s Strategic Investment Plan, the Investment Mandate is a
legislative instrument, but it is exempt from disallowance or sunsetting.[53] At that time the
Minister (former Minister Scullion) replied that the Government considered this
exemption was appropriate as it was consistent with other Investment Mandates
administered by the Future Fund Management Agency and provided certainty to the
Future Fund Board of Guardians in pursuing investments.[54]
Policy position of
non-government parties/independents
In his second reading speech on the Bill, Shadow
Attorney-General Mark Dreyfus stated that the Australian Labor Party would
support the Bill, based upon the extensive consultation with the Land Councils
that had taken place and the Land Councils’ expressed public support for the
Bill.[55]
The ALP Member for Solomon (NT) Luke Gosling subsequently expressed concerns
about some aspects of the Bill, including the wide discretion of the Minister
over the remaining balance of the ABA and the ABA’s investment strategy, but
continued to express overall approval.[56]
On 18 October 2021, during the Second Reading debate in
the House of Representatives, Leader of the Australian Greens Adam Bandt
expressed concern that the Bill had not been subject to a committee inquiry and
hence affected First Nations groups and communities had not had an opportunity
to be heard.[57]
The Bill was subsequently referred to the Senate Standing Committee on Finance
and Public Administration on its arrival in the Senate (see above).
Independent MP for Clark Andrew Wilkie expressed support
for the Bill but criticised the Government’s overall Indigenous policies.[58]
Position of major interest
groups
The Senate Standing Committee on Finance and Public
Administration inquiry has not yet published any submissions, so there has been
limited opportunity to assess the views of key stakeholders. According to the
Bill’s second reading speech and Explanatory Memorandum, the amendments
proposed have been extensively discussed with the NT Land Councils, the NT
Government, affected communities and mining peak bodies, amongst others.
Minister for Indigenous Australians, Ken Wyatt, noted that
the reforms have been ‘extensively co‑designed with traditional owners in
the Northern Territory and their land councils over the last 3½ years’ and that
the Land Councils have also consulted around 220 elected landowners whose land
generates ABA moneys as part of designing the reforms.[59]
A media release from Ministers Wyatt and McCormack quoted
Mr Sammy Bush-Blanasi, Chair of the Northern Land Council, as saying, ‘This is
a historic moment for Aboriginal Territorians - we will finally have control
over how money generated from mining on our land is spent. This will allow
Aboriginal people to invest in more Aboriginal jobs and support culture and
community for our grandchildren and beyond.’[60]
Financial implications
According to the Explanatory Memorandum, the NTAIC
measures will have a positive impact on the Commonwealth’s underlying cash
balance over time (as set out in the following Table 1).[61] This is presumably because
the NTAIC can be expected to make a higher return on its capital than the ABA.
However, this money will only be available at the direction, and for the
legislated purposes, of the NTAIC.
Table 1: Government estimates on underlying cash balance
| |
|
Impact on underlying cash ($ millions) |
| |
2020-21 |
2021-22 |
2022-23 |
2023-24 |
2024-25 |
Total |
| Expenditure |
0.0 |
+0.1 |
-0.4 |
-0.3 |
+1.0 |
+0.4 |
| Revenue |
0.0 |
-0.1 |
0.0 |
+3.2 |
+11.7 |
+14.7 |
| Total |
0.0 |
0.0 |
-0.4 |
+2.9 |
+12.6 |
+15.1 |
Source: Explanatory
Memorandum, Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Economic
Empowerment) Bill 2021, p. 9.
Statement of Compatibility with
Human Rights
As required under Part 3 of the Human Rights
(Parliamentary Scrutiny) Act 2011 (Cth), the Government has assessed the
Bill’s compatibility with the human rights and freedoms recognised or declared
in the international instruments listed in section 3 of that Act. The
Government considers that the Bill is compatible.[62]
Parliamentary
Joint Committee on Human Rights
The Parliamentary Joint Committee on Human Rights
considered the Bill in its 11th report of 2021 and made no comment.[63]
Key issues and provisions
Schedule 1
The first schedule’s amendments:
-
create a Northern Territory Aboriginal Investment Corporation
(NTAIC) (proposed Part VIA of the Act, consisting of proposed sections
65A to 65JE, as inserted by item 6, in particular see proposed
section 65B)
-
lay out its purposes, powers and functions (proposed sections
65BA–65BL)
-
establish a Board for the NTAIC alongside a procedure for
appointing the Board (a majority of which is elected by the four NT Land
Councils), CEO and Committee members (proposed Divisions 5 to 7, Part
VIA) and
-
guide the NTAIC’s investments according to a Strategic Investment
Plan, to be tabled in Parliament (proposed section 65C).
Key Issue: Creation of the NTAIC
The NTAIC is established with the purpose of both
promoting the self-management and economic self-sufficiency as well as the
social and cultural wellbeing of Aboriginal people in the NT (proposed
section 65BA). Its functions include making payments for the benefit of
Aboriginal people living in the NT and making investments in order to advance
its purposes (proposed section 65BB).
The NTAIC is given broad powers by the Bill, and it has
the power to do all things necessary or convenient for or in connection with
its functions (proposed section 65BD). This includes accepting gifts,
borrowing money, making loans, giving guarantees and entering other
arrangements. Many of the provisions note that the NTAI Corporation Rules (made
under proposed section 65JE) can provide details on the exercise of
these functions.[64]
Proposed section 65BH provides for an investment
limit so that the NTAIC cannot make an investment over $100 million without the
Minister’s agreement – this amount can be raised but not lowered by Ministerial
rules. The NTAI Corporation Rules can also set out how the ‘value’ of an
investment is calculated. The Government notes that this provision provides
appropriate Government oversight for very large investments, while safeguarding
the role of the NTAIC (as the limit cannot be lowered).[65] The Scrutiny of Bills
Committee noted that if such investment is erroneously made without the
Minister’s agreement, it is not invalidated (proposed
subsection 65BH(3)).[66]
The NTAIC is Commonwealth body corporate, and so will be
subject to the requirements of the Public Governance,
Performance and Accountability Act 2013 (PGPA Act) (proposed
subsection 65B(3)). Typically, a Commonwealth entity that makes
investments would be subject to an ‘investments mandate’ that outlines (among
other things) the expected ‘benchmark’ rate of return that it is required to
make, although this is not a legislative requirement of the PGPA Act.
Such Investment Mandates are often legislative instruments.[67]
The Bill instead provides that the Board must develop a
strategic investment plan (SIP) for the NTAIC which includes information on the
NTAIC’s priorities and principal objectives over a period of three to five
financial years (proposed section 65C). The SIP is not a legislative
instrument but is required to be tabled in Parliament (proposed subsection
65C(8)). Importantly, the Board must consult with both Aboriginal people
and Aboriginal organisations in the Northern Territory in developing the SIP (proposed
paragraph 65C(6)(a)), including Aboriginal people who are not Traditional
Owners and thus not represented by Land Councils. The Board must also consider
any advice given by the Investment Committee set up under proposed section
65FA (proposed paragraph 65C(6)(b)).
Part 2 of Schedule 1 puts in place
transitional arrangements by which members of an Interim Board are appointed by
the Minister and Finance Minister, Land Councils, and the Interim Board, until
full elections for the Land Council members of the Board can be held. This
Interim Board, rather than the first ‘regular’ board, will appoint the first
Independent board members and the first Investment committee, which is
responsible for creating the SIP.
To fund the NTAIC, approximately half ($680 million) of
the current accumulated balance of the ABA ($1.3 billion)[68] will be transferred to the
NTAIC over three years (proposed subsections 64AA(1)-(3) at item 4 of
Schedule 1). The Bill makes provision for further transfers in future, but
these are subject to ministerial discretion (proposed subsection 64AA(4)).
Item 5 also abolishes the current Aboriginals
Benefit Account Advisory Committee (ABAAC), meaning that ministerial
spending from the remaining balance of the ABA will be relatively unconstrained
in future (discussed below). A review of proposed Part VIA of the Act (which
would likely include a review of the NTAIC’s performance) after seven years,
which must be tabled in Parliament, is mandated by proposed section 65JD.
Key Issue: Tensions between
purposes of the NTAIC
The NTAIC’s purposes and functions, laid out in proposed
sections 65BA, 65BB and 65BC mandate, among other things, that:
65BA The NTAIC Corporation is established:
(a) to promote the self management and economic
self sufficiency of Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory; and
(b) to promote social and cultural wellbeing of
Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory.
65BB The NTAIC Corporation has the following functions:
(a) to make payments to or for the benefit of
Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory;
(b) to make investments for the purposes
mentioned in paragraphs 65BA(a) and (b);
(c) to provide financial assistance (other than
payments or investments of the kind mentioned in paragraphs (a) and (b) of this
section), whether on commercial terms or otherwise, to or for the benefit of
Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory
…
65BC General rules about performance of functions
In performing its functions, the NTAIC Corporation
must:
(a) have regard to its purposes under section
65BA; and
(b) have regard to the strategic investment
plan that is in force at the relevant time; and
(c) act in accordance with sound business
principles whenever it performs its functions on a commercial basis; and
(d) maximise the employment of Aboriginal
people living in the Northern Territory; and
(e) maximise the use of goods and services
provided by businesses owned or controlled (whether directly or indirectly) by
Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory.
Thus the NTAIC must act for beneficial or charitable
purposes by promoting social and cultural wellbeing (proposed
paragraph 65BA(b)) and making beneficial payments (proposed
paragraphs 65BB(a) and (c)). It must also act as a long‑term
investment manager (proposed paragraphs 65BA(a), 65BB(b), 65BC(b) and
(c)). In making its investments it is in many ways constrained to investing
in Aboriginal‑related enterprises in the Northern Territory by the
effects of proposed paragraphs 65BC(d) and (e). The NTAIC’s
stakeholders will likely expect the NTAIC to have funds available to make
grants which do not generate direct business returns (proposed paragraphs
65BB(a) and (c); although for these purposes, the Minister may
provide supplemental funds from the ABA). This combination of purposes reflects
the Government’s intention that the Bill provides the NTAIC with broad
functions that it can perform on a commercial or non-commercial basis as
appropriate.[69]
While this combination of purposes has the potential for a
‘multiplier effect’ of positive outcomes through the combination of directed
investment and direct action, it also means that the NTAIC’s investments may be
heavily exposed to the high-risk business environment of Northern Australia,
particularly to Indigenous-owned and community enterprises. As the Joint
Standing Committee on Northern Australia Inquiry into the Opportunities and
Challenges of the Engagement of Traditional Owners in the Economic Development
of Northern Australia has heard,[70]
the Northern Australia business environment faces many challenges and these are
particularly acute for Indigenous businesses, meaning that existing investment
facilities such as the Northern Australia Infrastructure Facility have
struggled to find commercially viable projects within its risk appetite.[71]
In addition, the NTAIC may be investing in many businesses
at a very early stage of development. While the SIP will presumably seek to
diversify the NTAIC’s portfolio, it is not clear whether investment under the
SIP is permitted to go outside the sectoral constraints of proposed
paragraphs 65BC(d) and (e). This sectoral exposure runs the risk
that significant portions of the NTAIC’s capital could be lost if a ‘flagship’
investment performed badly (for example, the Indigenous Land Corporation’s
significant loss of capital when the value of Ayers Rock Resort was written
down)[72]
or if some external event affected the NT’s economy (for example, local
recession, or natural disasters such as cyclones or the COVID-19 pandemic with
their impact on tourism-dependent economies).
As the Land Councils and their associated commercial and
investment entities, such as CentreCorp and the Aboriginal Investment Group
(AIG), are also operating in the constrained investment environment of the NT,
managing potential or perceived conflicts of interest between these various
associated entities may be challenging. Recent controversies around the lease
of AIG buildings in Darwin by the Northern Territory Land Council provide one
example.[73]
Given that the NTAIC is required to ‘maximise the use of goods and services
provided by businesses owned or controlled (whether directly or indirectly) by
Aboriginal people living in the Northern Territory’,[74] many of which are associated
with Land Councils, such intersections of interests may occur frequently.
Key Issue: Representativeness
and election of the NTAIC Board
Under proposed section 65EA, the NTAIC is to be
governed by a board consisting of two members from each of the four Northern
Territory Land Councils, two members appointed by the Minister and the Finance
Minister, and two independent members appointed by the Board.
Professor Altman has raised concerns[75] that this representation
formula significantly differs from the ABA Advisory Committee (ABAAC)
membership, which currently advises on expenditure under section 65 of the Act.
The ABAAC currently comprises eight members (including the co-chair of the
ABAAC) from the Northern Land Council (NLC), five from the Central Land Council
(CLC), one member from each of the Tiwi Land Council (TLC) and Anindilyakawa
Land Council (ALC), and a ministerially appointed chair.[76] These ABAAC land council
memberships are in some proportion to the Aboriginal population of the area
represented by each land council (see Table 2 below). The Bill’s proposed
membership of the NTAIC Board gives disproportionate weight to the small TLC
and ALC, which may in turn lead to disproportionate investment or expenditure
by the NTAIC in those areas of the NT at the expense of other areas. This is
further highlighted in Table 2 below.
The Explanatory Memorandum provides no explanation for
this weighting of Board seats, instead simply stating that drawing the Board’s
membership from the Land Councils ‘ensures consistency with the architecture of
the Land Rights Act, whereby ABAAC representatives were drawn from the Land
Council membership’.[77]
One possible rationale for this seat distribution is that, if the Government
and Independent members of the Board all opposed a motion, it would only take
one Land Council siding with the Government and Independent members for it to
fail.
Table 2: Comparison of seats on the ABAAC and the proposed
NTAIC Board
| Land Council |
Aboriginal popn. of area
(approx.) |
Seats on ABAAC |
Seats on NTAIC Board |
| NLC |
51,000 |
8 (inc. co-chair) |
2 |
| CLC |
24,000 |
5 |
2 |
| TLC |
2,700 |
1 |
2 |
| ALC |
1,500 |
1 |
2 |
| Government/Independent
Members |
- |
1 |
4 |
| Total |
79,200 |
16 |
12 |
Source: Population estimates
have been taken from the relevant Land Council webpages.
Professor Altman also expressed concern that despite the
NTAIC being established to make investments and payments to or for the benefit
of all Aboriginal people of the Northern Territory, there is no Board
representation of the non-Traditional Owner Aboriginal population of the NT.[78] However, in this
regard, the NTAIC replicates the existing makeup of the ABAAC.
The procedures for electing members to these key positions
are also largely undefined by the Bill. Proposed subsection 65EB(4)
states that ‘A Land Council must conduct an election for the purposes of making
an appointment under subsection (1) [to the board of the NTAIC]. The Land
Council may determine the manner in which the election is to be conducted.’
This contrasts with the requirements of subsection 29(1) of the Act for
electing Land Council members, who are to be ‘chosen by Aboriginals living in
the area of the Land Council in accordance with such method or methods of
choice, and holding office on such terms and conditions, as is, or are,
approved by the Minister from time to time’, thus ensuring that the process has
external oversight via the Minister.
With the Land Councils being granted this flexibility, it is
not clear why an election, rather than a simple ‘choice’ or ‘appointment’, is
mandated in the Bill. Furthermore, while allowing the Land Councils to
determine the manner of the election is in keeping with the goal of
self-determination, and may make pragmatic sense given the logistical
difficulties faced by some Land Councils in coordinating meetings and elections
across many remote communities, the Bill as it stands does not mandate
openness, procedural fairness, or consistency of election conduct from one
election to the next. This raises the possibility that the electoral process
could be manipulated.
Such a possibility could arguably be averted by requiring
the Land Councils or NTAIC to issue written instructions for the conduct of
Board elections as part of the Board’s Code of Conduct (under proposed
section 65EM), which would increase transparency without reducing the
self-determination of the Land Councils. If external oversight or the
possibility of it is required, amendments authorising the Minister to issue
such instructions as part of the NTAIC Corporate Rules under proposed section
65JE could arguably permit this — which would still allow procedural
flexibility but provide for ministerial oversight.
Key issue: Payments by the NTAIC
and their tax treatment
Currently, payments from the ABA for beneficial purposes
under subsection 64(4) of the Act may incur Mining Withholding Tax (MWT), an
income tax (currently set at 4%) levied specifically on Indigenous recipients
of mining payments by Division 11C of the Income Tax
Assessment Act 1936.[79]
Broadly speaking a mining payment is an amount that represents
royalties which have been received by the Commonwealth for the mining of
Indigenous land.[80]
As a withholding tax, although formal legal liability for MWT rests with the
Indigenous recipients, the actual responsibility for paying the MWT rests on
the person or entity who makes the payment: such bodies are required to
withhold an amount from a mining payment in accordance with the
Pay As You Go (PAYG) withholding rules.[81]
In the case of grants made under subsection 64(4), this body is the ABA.
Not all of these payments incur this tax liability, as
payments made out of the investment earnings of the ABA are not mining
payments and hence do not attract MWT. It has become the practice of
the managing agency (currently NIAA) to make section 64(4) payments out of the
investment earnings where possible, so as to minimise the MWT liability of the
recipients of those payments.[82]
However, some payments of MWT for this purpose are still made.[83]
The NTAIC has now been empowered to make beneficial
payments under proposed paragraphs 65BB(a) and (c), a
function for which the Minister may provide them with additional
payments from the ABA under proposed subsection 64AA(4). The Explanatory
Memorandum states that the function of making beneficial payments will now pass
to the NTAIC and beneficial payments will cease to be made from the ABA
(although the Bill does not mandate this – see discussion below).[84] Beneficial
payments made by the NTAIC under proposed paragraphs 65BB(a) and (c) would
appear to not be mining royalty equivalents per se (and hence not mining
payments). It therefore appears that such payments would not impose a
MWT liability on the Indigenous recipients of such payments. The overall
practical effect of the policy change from beneficial grants being made by the
ABA to beneficial grants being made by the NTAIC, for the Indigenous
end-recipients, is that MWT is unlikely to be paid on any such beneficial
grants received from the NTAIC. While the Bill does not amend the application
and operation of MWT under tax legislation and the amounts at stake are not
large, this policy change is of interest given that Land Councils and other
stakeholders have often decried the MWT as an unjustified impost.[85]
Key Issue: The balance of the
ABA and absence of an ABA investment strategy
Since 2006, the combination of rising world mineral prices
(and hence mining royalties) and increased retention of funds in the ABA, as a
result of both ministerial decisions to build the account’s equity, and the
reduced payments to Land Councils stemming from the 2006 amendments, has
resulted in a large balance accumulating in the ABA.[86] On 30 June 2005, the balance
of the ABA was $102.9 million;[87]
since then, it has risen to exceed $1.3 billion.[88] The graph below shows the
increasing balance of the ABA compared to its static level of beneficial
(section 64(4)) expenditure in recent years.
Increasing balance of the ABA, 2015–2019
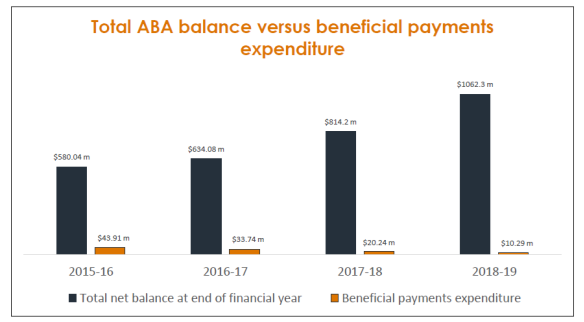
Source: NIAA, Supplementary
Submission, op. cit., p. 5.
While maintaining an invested equity reserve in the ABA is
a legitimate and statutory (under section 62A) purpose of the ABA, particularly
considering its dependence on potentially unpredictable and exhaustible mining
revenues, retention of an ever-increasing balance has effectively imposed a
large opportunity cost upon the Aboriginal population of the NT whom the ABA is
intended to benefit. Furthermore, owing to the requirements of the PGPA Act[89] for investing
public funds, the balance of the ABA can only be invested in cash accounts,
term deposits or investment-grade securities such as government bonds.[90] Since 1976, when
the Act was passed, and particularly since the global financial crisis (which
occurred shortly after the 2006 Amendments took effect), the return on such
investments has declined from 10 per cent or more per annum to less than three
per cent per annum.[91]
There is therefore a strong case for reconsidering
management of the ABA and investing the balance in ways which will better
benefit Traditional Owners and the Aboriginal people of the NT. The Bill
accomplishes this in part by creating the NTAIC, which will be empowered to
make investments outside the constraints of section 59 of the PGPA Act
by proposed subsection 65BG(2).[92]
However, a substantial balance ($620 million or more) will remain in the ABA.[93] Without any
change in its investment strategy, the remaining balance in the ABA will thus
continue to earn extremely low returns for the immediately foreseeable future.
Furthermore, as Professor Altman[94]
and former CEO of the ILC Michael Dillon[95]
have both observed, the ABA’s mining royalty equivalent income is likely to
sharply diminish in the near future, as the Groote Eyelandt manganese mine,
which currently provides approximately two-thirds of the ABA’s royalty
equivalent income, is scheduled to close within five years.[96] Under these circumstances, a
higher‑return investment strategy may be the only way for the ABA to
fulfil its legislated functions of providing for Land Council operating
expenses.
The former Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Land
Account (the Land Account) provides an interesting comparison in reform of
government special accounts in the Indigenous policy space. Like the ABA, the
Land Account had low returns (which threatened its long-term sustainability)
owing to the requirements of the PGPA Act. The government’s response to
this was to create a new Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Land and Sea
Future Fund (ATSILSFF), which is invested by the Future Fund Management
Authority (FFMA).[97]
Unlike the ABA’s transfer of half its balance to the NTAIC, the entire
balance of the Land Account was transferred into this new investment vehicle.
Conversely, unlike the NTAIC, the FFMA is under no obligation to invest these
funds in ways which are beneficial to Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander
people, other than by producing a sustainable dividend for use by the
Indigenous Land and Sea Corporation, and has no significant Indigenous input or
control into its investment and governance.[98]
The expressed preferences of many Indigenous stakeholders at the time that the
ATSILSFF should be required to take wider Indigenous interests into account,
for example by investing according to the Indigenous Investment Principles,[99] were rejected by
the FFMA and the Commonwealth.[100]
Like the Bill, the creation of the ATSILSFF also removed
without replacement the previous Indigenous oversight body – in that case the
Consultative Forum on investment policy of the Land Account, which had been
convened under former section 193G of the Aboriginal and
Torres Strait Islander Act 2005,[101]
and in this case the ABAAC. However, in the case of the NTAIC, the Land
Councils, through the NTAIC Board, will exercise a determinative, not merely
advisory, role over the half of the ABA’s accumulated balance that passes to
their control, and appear to regard this as a worthwhile trade-off.
Key Issue: Increased Ministerial
control over the remaining ABA balance
Item 5 of Schedule 1 repeals section 65 of
the Act. This section creates and governs the Aboriginals Benefit Account
Advisory Committee (ABAAC). Subsection 65(1) currently states ‘There shall be
an Account Advisory Committee to advise the Minister in connexion with debiting
the Account for the purposes of making payments under subsection 64(4).’
The ABAAC is thus the statutory advisor on the Minister’s
power to make payments from the ABA under section 64(4) of the Act (‘There must
be debited from the Account and paid by the Commonwealth such other amounts as
the Minister directs to be paid or applied to or for the benefit of Aboriginals
living in the Northern Territory’). Repealing section 65 has the effect of
abolishing the ABAAC.
For some years, the practice has been that section 64(4)
payments are made through a departmental grant program with grants usually
(though not always) assessed and recommended by both the Department and the
ABAAC before being forwarded to the Minister. The NIAA webpage, ABA Grants
Information and Application Process states:
The Agency assesses every compliant application received by
the closing date.
The Agency provides its assessment to the ABAAC for their
consideration. The ABAAC reviews the proposal and provides advice to the
Minister.
The Minister uses this information when deciding which
applications will proceed to the negotiation of a funding agreement.[102]
The ABAAC only has an advisory function, and the
Minister is not obligated to follow its advice, even under the current
framework. However, the fact that the ABAAC is a legislated body under current
section 65 may mean that if a Minister were to make payments which were
obviously against ABAAC advice, such decisions could possibly be subject to
judicial review and would likely face public scrutiny. The Bill’s abolition
without replacement of section 65 means that payments from the balance of the
ABA (which, even after the Bill’s deductions to endow the NTAIC, will still
exceed $600 million) under section 64(4) would be solely at the discretion of
the Minister, without any legislated scheme for advice put in place. The
practical (albeit not legal) constraint provided by ABAAC on the Minister’s
discretion would therefore be removed.
The Explanatory Memorandum to the Bill states that the
function of making beneficial grants will now pass to the NTAIC:
With the NTAI Corporation established to make payments to or
for the benefit of Aboriginal people in the NT, it will replace the ABAAC and
empower Aboriginal Territorians to make the payments.[103]
The NTAIC is granted the power to do so by proposed
paragraph 65BB(a) (at item 6 of Schedule 1). The
implication is that the Minister through the relevant agency (currently the
NIAA) will no longer make such payments. However, there is no provision in the
Bill which prevents the Minister from making such payments out of the ABA.
Furthermore, the NTAIC would have financial constraints
upon its grant-making ability which would not apply to the Minister. After
approximately the first two years of operation (during which the NTAIC receives
payments totalling $680 million under proposed subsections 64AA(1)–(3)),
the NTAIC does not receive a guaranteed income from the ABA (with which to make
such grants, or for any other purpose). It must instead fund beneficial
payments either from the return on its investments (which it may wish to
retain, in order to protect the investment capital) or by relying on additional
debits from the ABA at the Minister’s direction (having regard to recent
estimates of the NTAIC’s expenditure) (proposed subsection 64AA(4)).[104]
Under proposed subsection 64AA(4), the Minister
must grant to the NTAIC ‘such amounts as the Minister directs from time to
time’. While this is the same language used to provide for the annual
budgets of the Land Councils under section 64(1), it is nevertheless not a
strong stipulation; it is not required to be annual, nor is any minimum amount
or proportion of the ABA’s mining royalty equivalent income specified by the
section (in contrast to the minimum payments to Traditional Owners under made
under section 64(3) of the Act).[105]
While the NIAA has stated that such payments will be made annually, the Bill
itself does not prescribe this.[106]
Furthermore, the Explanatory Memorandum explicitly states:
Section 64AA(4) is intended to provide a mechanism for
ongoing funding to the NTAI Corporation, whilst balancing its funding needs
with the availability of funding from the ABA. Whilst the Minister must
have regard to certain estimates when making directions under section
64AA(4), this does not preclude the Minister making a direction for an
amount that differs from those set out in the estimates.[107] [emphasis added]
This contrasts, for example, with funding of the
Indigenous Land and Sea Corporation, which receives annual payments of amounts
stipulated by section 22 of the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Land
and Sea Future Fund Act 2018.[108]
Thus, under the proposed amendments, despite the
descriptive intent of the Explanatory Memorandum, the Minister would retain the
power to make grants from the existing ABA under subsection 64(4), without
being advised by the ABAAC. The Minister is not required to grant money
with any regularity to the NTAIC for the purposes of beneficial grants, and
could effectively limit the NTAIC’s grant budget by making smaller payments
than requested, using their discretion under proposed subsection 64AA(4).
There could be potential political incentives for a Minister to retain grant
giving power and money using this mechanism. As a number of controversial
payments out of the Indigenous Advancement Strategy and ABA funds by former
Minister Scullion showed, the range of payments which a Minister might claim
were ‘for the benefit of Aboriginals living in the NT’ under s 64(4) could be
quite broad.[109]
Commonwealth grants programs have come under increasing
scrutiny for their purported/alleged use for political purposes in recent times
(see, for example, recent commentary around the Community Sport Infrastructure
Grant Program and the Commuter Car Park Program). These political controversies
have led to calls for reforms to the legal and administrative frameworks that
govern Commonwealth grants.[110]
In this environment, it should be noted that the removal of the ABAAC’s
advisory function may in practice lead to increased Ministerial
discretion in relation to the allocation of payments from the ABA than is the
case under the current framework, although, owing to the transfer of half of
the balance of the ABA to the NTAIC, the amount which the Minister controls is
reduced.
Of Interest: Power of the Minister to approve the CEO
The Board of the NTAIC is only able to appoint (proposed
section 65GB) or terminate (proposed section 65GI) a CEO with the
written agreement of the Minister. This contrasts with the CEOs of the
comparable Indigenous Land and Sea Corporation (ILSC) and Indigenous Business
Australia (IBA), both of which are appointed solely by the Boards of those
corporations (see sections 168 and 192K of the Aboriginal and
Torres Strait Islander Act 2005). The Explanatory Memorandum states
that this ‘ensures Commonwealth oversight of the appointment’ without
explaining why this additional oversight is considered necessary.[111]
Schedule 2 Amendments: Mining
related decision making
The second schedule implements several amendments
recommended by the Aboriginal Land Commissioner’s 2013 Review of Part IV of
the Aboriginal Land Rights (Northern Territory) Act 1976 concerning mining
activity under the Act.[112]
These amendments update the Act to reflect relevant Northern Territory
legislation and developments in mining (such as those concerning geothermal
energy), clarify and change aspects of the approval process (including meeting
consent requirements with Traditional Owners), clarify the process for dealing
with relatively low impact mining for extractive minerals (clay, gravel, sand,
et cetera), and change parts of the Ministerial delegation and approval process
by removing delegation of some Commonwealth ministerial approvals to the
Northern Territory mining Minister and removing the requirement for
Commonwealth ministerial approval for some mining projects.
Item 21 makes amendments to enable a Land Council
to determine whether an exploration application does or does not substantially
comply with the legislated application requirements under subsection 41(6), and
provides the applicant with the opportunity to vary or resubmit their
application in a compliant form. Currently the relevant provision (subsection
41(6A)) simply states that strict compliance with the legislated requirements
is not required and ‘substantial compliance’ is sufficient, without explicitly
enabling the Land Council (or any other party) to determine what constitutes
‘substantial’ compliance. This amendment was not the subject of a
recommendation in the 2013 Review, but the increased procedural flexibility
would seem to be in the interests of all parties.
Item 23, inserting proposed subsection 42(4),
grants Land Councils slightly greater power to determine whether meetings with
the Traditional Owners are convened to discuss an application, or a variation
of an application, in line with Recommendation 6 of the 2013 Review.[113] The 2013
Review noted that such an amendment would be in the interests of efficiency and
timely addressing of applications.[114]
In the light of recent disputes between, for example, the
Northern Land Council and persons who were, or claimed to be, traditional
owners in the Beetaloo Basin, this proposed subsection may be of particular
interest to Parliament.[115]
Currently paragraph 42(4)(a) mandates that ‘the Land
Council shall convene such meetings with them [Traditional Owners] as are
necessary for the purpose of considering the exploration proposals and the
terms and conditions’.
The proposed subsection reads:
42(4) To facilitate consultation between the Land Council
and the traditional Aboriginal owners, the Land Council must:
(a) subject to
subsection (4A), convene such meetings with them, after the Land
Council determines under subsection 41(7) that it is satisfied the
application complies substantially with subsection 41(6), as the Land
Council considers appropriate for the purposes of considering the
exploration proposals and the terms and conditions…[emphasis added]
While noting that current paragraph 42(4)(a) might already
give Land Councils the flexibility to determine that a meeting is not
necessary, proposed paragraph 42(4)(a) gives the Land Council greater
freedom to determine whether holding a meeting with Traditional Owners is or is
not appropriate, which might conceivably work against Traditional Owner
interests if a Land Council were to restrict meetings in order to prevent
objections to a mining project. In other words, the amendments appear to make
the question of requiring a meeting with Traditional Owners as a question to be
solely determined in the view of the Land Council (that is, what the Land
Council considers appropriate for the exploration proposals and terms
and conditions to be considered becomes the key factor). Under the current
framework, arguably, such meetings may be required where considered objectively
‘necessary’ for considering proposals and terms and conditions. The amendments
may give the Land Council more power in this regard.
Proposed subsection 42(4B) also grants extra
decision-making flexibility to Land Councils, potentially at the expense of
Traditional Owners, by enabling Land Councils to accept variations to an
application after the original application has been discussed by Traditional
Owners, without holding a meeting to consider the varied application, as long
as the relevant matters were discussed at one or more of the original meetings.
One could easily imagine situations in which Traditional Owners might consent
to an original application but not to some variation of it.
However, these proposed subsections are still subject to
sections 42(2) and 42(6) of the Act (as amended by the Bill):
42(2) The Land Council must not consent to the grant of
the licence unless it has, before the end of the negotiating period, to the
extent practicable:
(a) consulted the
traditional Aboriginal owners (if any) of the land to which the application
relates concerning:
(i) the exploration proposals; and
(ii) the terms and conditions to which the grant of the licence may be
subject; and
(b) consulted any
Aboriginal community or group that may be affected by the grant of the licence
to ensure that the community or group has had an adequate opportunity to
express to the Land Council its views concerning the terms and condition
…
42(6) Subject to subsection (7), the Land Council
must not consent to the grant of the licence unless:
(a) it is satisfied
that the traditional Aboriginal owners (if any) of the land understand the
nature and purpose of the terms and conditions and, as a group, consent to
them;
(b) it is satisfied that the terms and conditions are reasonable; and
(c) it has agreed with the applicant upon the terms and conditions.
Thus Land Councils would still be bound by the requirement
to be satisfied that the Traditional Owners as a group consented to the
original licence and its terms and conditions, and the requirement to be
satisfied that those terms and conditions were reasonable. If Land Councils
were to use the proposed increased procedural powers and flexibility to
circumvent Traditional Owner consent (for example by considering that a meeting
was not ‘appropriate’ and so not holding one) they would risk the grant of a
licence being found invalid under subsections 42(2) or 42(6).
Item 25 make amendments that remove the requirement
for Commonwealth Ministerial consent to an exploration licence after the Land
Council has consented. This is a strengthening of Aboriginal decision-making
power, as it prevents the Minister overruling a decision of the Land Council,
and also removes a potentially significant delay (up to 30 days) from the
application process, which could otherwise cause significant and unnecessary
expense to applicants.
However, it does remove a potential check-and-balance from
the current licence granting process, inasmuch as the Minister may consider
other factors (such as submissions from minority Traditional Owners, or from
other non-Traditional Owner Aboriginal people affected by a development, or any
other factors), which a Land Council is not bound to consider. Similarly, the
Minister may believe that a Land Council or Traditional Owner is being in some
way deceived or short-changed by an applicant, or in some other way the
national interest is not served by granting a licence. For this reason the
proposal to remove this section was opposed by Land Councils at the time of the
2013 Review.[116]
However, Recommendation 9 of the 2013 Review recommended that consideration
should be given to whether the Ministerial consent requirement added ‘quality’
to the approval process and, if it did not, to repealing it, with the
Commissioner noting that the current lack of substantive information provided
to the Minister on a licence decision mean that it is not an effective
‘backstop’.[117]
It appears that the result of this consideration has been to repeal the consent
process.
The Minister does retain powers under section 47 of the
Act to cancel exploration licences or mining interests if the exploration or
mining is not, or is likely not to be, in accordance with the terms and
conditions, and is having or is likely to have significant impacts on the
affected land and Aboriginal peoples. Therefore the Minister retains an
‘emergency override’ power.
This ‘emergency override’ federal power is effectively
strengthened by item 51 which widens the scope of matters which cannot
be delegated to the Northern Territory Mining Minister from only those parts of
subsections 47(1) and (3) explicitly concerning the national interest, to all
of subsection 47(1) (exploration) and subsection 47(3) (mining) powers. As the
2013 Review noted, the federal Minister for Indigenous Australians is more
likely to be able to consider the environmental, social and cultural factors at
stake than the NT Mining Minister.[118]
Other Ministerial powers in Part IV do not appear to be
affected by the Bill. For example, where consent is refused and the application
is placed into moratorium for five years, a Land Council can still apply to the
Commonwealth Minister to recommence negotiations (subsection 48(3)). In
addition, Northern Territory law will still require consent to be given by the
Northern Territory Minister to commence negotiating with the Land Council (see,
for example, section 62 of the Mineral Titles Act 2010[119] or section 13 of the Petroleum
Act 1984).[120]
This requirement is provided for in Commonwealth legislation by subsection
41(1) of the Act.
Item 36 of Schedule 2 to the Bill, proposing replacement
subsection 44A(1), enables the terms and conditions of an exploration
licence to include compensation for the value of minerals removed or proposed
to be removed. This is precluded under current subsection 44A(1) of the Act.
This reform is necessary because of previous reforms to
the mining approval process first introduced in the Aboriginal Land Rights
(Northern Territory) Amendment Act (No 3) 1987.[121] Before that time, two
approval processes were needed for mining-related activity on Aboriginal land;
approval for exploration, and then approval for mining. This dual approval
process was objected to by mining companies, as it meant that they might
potentially find a valuable deposit while exploring but be forbidden from
exploiting it.[122]
The 1987 Amendments conjoined these processes so that only one approval (or
veto) from Traditional Owners was needed or could be exercised, although there
are still separate agreement-making processes for exploration and mining.
This conjoined process created its own problems, as
Traditional Owners sought details of any proposed mining activity in the
exploration permission application before granting it, lest they find
themselves consenting to mining projects without knowing the details. It is
clearly difficult for companies to predict what the scope of a mine might be,
when they have not yet done any exploration and so do not know what minerals,
in what geographical and geological location, are in situ. Another
result was that exploration agreements ended up including agreements on mining
royalty terms in the event that exploitable resources were found, a practice
which potentially contravened current subsection 44A(1).
The 2013 Review discussed this situation at length but did
not recommend any changes to the approval and veto process at this stage, other
than by amending subsection 44A(1) to recognise current practice
(Recommendation 13).[123]
Schedule 3
Schedule 3 of the Bill makes changes to land
administration and control processes including those for township leases, land
in escrow, ministerial approvals, and control over access to Aboriginal land.
In part these reverse or alter contentious amendments made in 2006 and 2007.
Key Issue discussion: Township Leases
The purpose of Part 1 of Schedule 3 is to enable community
corporations (CATSI corporations) formed under the Corporations
(Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander) Act 2006 (CATSI Act),
rather than the Executive Director of Township Leasing (EDTL), to hold the
head-lease of townships on Aboriginal land rights land. Such arrangements
already exist for the towns of Gunyaŋara
and Jabiru,
the first being enabled by Ministerial approval and the latter by amendments to
the Act passed in 2020 (the Aboriginal Land
Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Jabiru) Act 2020) as part of the
handback of Jabiru to the Mirrar Traditional Owners.[124] Similar arrangements are in
train in Muṯitjulu and Pirlangimpi (the Muṯitjulu
lease is a sublease of the Uluru Kata-Tjuta national park, rather than a
township lease under the Act).[125]
The Bill proposes a statutory process for the approval of
CATSI corporations to become the head-leaseholders of townships, in place of
these one-off arrangements. The proposed statutory process provides greater
clarity on requirements to be met for this approval, including:
-
the relevant Land Council has nominated the CATSI corporation (proposed
paragraph 3AA(2)(a))
-
members of the corporation are either the Traditional Owners for
all or part of the area or are Aboriginal people who live in the area (proposed
paragraph 3AA(2)(b)).
Issues relating to the township leasing model
Township leasing under the Act was established by the 2006
Amendments and the subsequent Aboriginal Land
Rights (Northern Territory) Amendment (Township Leasing) Act 2007.[126] Leases
have been usually administered by the Executive Director of Township Leasing
(EDTL) and the Office of Township Leasing (OTL). They are intended to be a
means by which Aboriginal traditional owners in the NT can leverage benefits
such as individual home ownership for Aboriginal people and market rental
payments through the application of a managed sub-leasing scheme.[127]
According to the 2018–19 Annual Report of the Executive
Director of Township Leasing, the OTL held leases over eight townships, 26
housing developments, 17 Alice Springs town camps, and administered the leases
of 74 parcels of land used for Commonwealth assets.[128] The OTL claims that these
leases were actively contributing to economic development and individual home
ownership in many of these towns.[129]
The expenses of the OTL and of Commonwealth leases over land are paid out of
the ABA, instead of government consolidated revenue, a practice which has
frequently attracted criticism.[130]
Professor Altman has calculated that over the course of its existence since
2007, the OTL has cost the ABA approximately $50 million (some of which was
payments to Traditional Owners), while recouping $17 million in rent.[131]
Township leasing was originally established in the 2006
Amendments, and then augmented in 2007, as part of a package of reforms which
were hostile to the communal nature of land rights and the power of the large
land councils. The Howard Government and numerous commentators believed that
economic development required the introduction of individualised, tradable and
bankable property titles in towns and settlements on Aboriginal land. The two
larger land councils perceived the township leases, in combination with
provisions which could see them delegate their powers to local CATSI
corporations and the 2007 Northern Territory Emergency Response which imposed
compulsory five-year leases in many communities, as an attack on land rights,
and so were hostile to their introduction. For many years the only township
leases taken up were in the Tiwi and Groote Archipelagos covered by the smaller
land councils. Township leasing was not a policy priority for the 2007–2013 ALP
Government and so no new township leases were signed during that time, although
many new section 19 leases were established to provide secure tenure for public
housing and infrastructure investment.[132]
When the Coalition returned to power in 2013, it
recommenced negotiations with the mainland Land Councils and eventually adopted
a model of ‘community led’ township leasing that was proposed by several
Aboriginal leaders including Galarrwuy Yunupingu. The first such lease was
established in 2017 over Muṯitjulu as a sublease from the Uluru
Kata-Tjuta National Park, rather than a township lease under the Act. It is
still being managed by the EDTL while a community entity builds capacity for a
takeover of the lease.[133]
Jayne Weepers, Visiting Fellow at the Centre for
Aboriginal Economic Policy Research (Australian National University) notes that
despite the stated intent of township and other such leases being to promote
private economic development, the vast majority (~90%) of township subleases
and section 19 leases in CLC land have been taken out by government
entities (Commonwealth, territory and local), with the remainder largely taken
up by NGOs (many of which would be providing contracted quasi-governmental
services, for example, running Community Development Programs).[134] The major
economic effect, rather than promoting private enterprise, has been an
increased income stream for Traditional Owners from rental payments, the
majority of which is directed to community beneficial projects run by the land
councils or the town CATSI corporations. Thus the net effect of land reforms so
far has been to entrench the role of governments and land councils,
rather than promoting private sector alternatives.[135]
This may support the position of many stakeholders,
including the NLC and CLC, who have argued that barriers to private sector
development in remote communities are not linked to whether tenure is
‘communal’ or ‘private’, but to the more prosaic factors of distance and local
poverty, and the resulting lack of economic opportunities.[136] Given the relatively early
stages of such tenure changes, it is still possible that they will support more
private sector development in future, particularly given that leases may now be
perceived as community-led, rather than imposed.
Stakeholder concerns on township leasing reforms in the
Bill
Some commentators have raised other concerns about this
Part of the Bill. As discussed above in this Digest, the Scrutiny of Bills
Committee raised concerns that whether an entity became ‘approved’ is largely
left to the Minister to determine via legislative instrument under proposed
subsection 3AA(9). However, it should be noted that the Minister can only
approve entities if they are incorporated under the CATSI Act, have been
nominated by the local Land Council, and if a majority of the CATSI
Corporation’s members are traditional owners or Aboriginal people living in the
community (proposed subsection 3AA(2)). In addition the Land Council
must furnish the Minister with reports on local consultations when making a
nomination (proposed subsection 3AA(5)(f)).
On the form of an approved entity, Altman notes:
In Schedule 3, [proposed section] 3AA an approved entity to
hold a s19A township lease can have membership of ‘Aboriginal people who live
in the area of land known by that name’ rather than being limited to the
traditional Aboriginal owners of land. This raises the possibility that a
corporation that is made up of non-traditional owners and possibly Aboriginal
people who are recent arrivals in the NT could be the legally recognised
landlord of a 99-year lease over Aboriginal freehold land. This possibility
needs careful re-evaluation and amendment.[137]
In many communities non-traditional owners are the
majority of the Aboriginal population, owing to historical displacement to
former missions, government settlements, ration stations or pastoral
properties. The tensions and compromises this has given rise to in communities
are described at greater length in Weepers’ paper.[138]
Michael Dillon has raised concerns about the commercial
practicality of CATSI corporations holding head leases:
While they appear to provide greater community control over
the township tenure, the use of local corporations rather than a government
entity to hold the head lease means that potential lenders will be much less
willing to lend to sub-lessors because in the event of a loan default, the
mortgaged land will only revert to the lender while the local corporation
remains solvent. Solving this potential problem was the reason that the EDTL
was established in the first place. The Minister should provide a detailed
explanation of how he intends to address this issue as potential lenders will
vote with their feet and not lend in circumstances where they cannot be
guaranteed access to the mortgaged land.[139]
While this issue is not explicitly addressed by the Bill, proposed
subsection 3AA(7) enables the Minister to revoke a lease, which would
provide an option if the CATSI corporation became insolvent. The Explanatory
Memorandum notes ‘[e]xisting leases have mechanisms that provide for the
surrender of the lease or the transfer of the lease to another approved entity,
prior to a lease being terminated’[140]
– thus, leases could be written so as to make the EDTL the ‘head lease holder
of last resort’ in the event of insolvency. It should also be noted that under proposed
section 19B (at item 7 of Schedule 3 to the Bill), approved
entities can have their expenses for acquiring and administering leases met out
of the ABA after submitting estimates for approval to the Minister; thus, an
approved CATSI corporation holding a head-lease would not need to make a profit
in order to remain solvent.
Other amendments in Schedule 3
Part 2 of Schedule 3 of the Bill contains
amendments allowing Land Councils to enter agreements in respect of land that
is the subject of a deed of grant held in escrow.
Land in escrow proposals have apparently arisen out of
negotiations over the post-mining future of the Gove Peninsula, according to
the Explanatory Memorandum.[141]
Detail on the operation of the amendments is provided at pages 54–56 of the
Explanatory Memorandum.
Part 3 of Schedule 3 contains various miscellaneous
amendments.
Items 30 and 32 of the Bill repeal sections
28A to 28F of the Act (and other referring subsections), which originally
permitted a Land Council to delegate various powers and functions (including
exploration and mining permissions) to a local CATSI corporation. These
provisions were inserted by the 2006 Amendments. At the time, they were part of
an overall policy to push the Land Councils to delegate many of their functions
to local bodies (including approvals for mining), in accordance with the
controversial recommendations of the 1998 Reeves Review.[142] Their repeal, along with the
repeal of other provisions which were seen as potentially weakening Land Council
control such as 74AA (repealed by item 36)[143] is presumably a sign of the
more cooperative relationship with the Land Councils pursued by the current
Government, as well as a response to the access concerns caused by the Covid-19
pandemic. This cooperative relationship is perhaps also evidenced in the
amendment made by item 29 which will expand the value of contracts that
Land Councils can enter into without ministerial permission – from a current
value of $1 million to $5 million.
Key Issue: Baniyala Nimbarrki Land Authority
The Explanatory Memorandum states that the provisions for
delegation of Land Council powers and functions to CATSI corporations (sections
28A to 28F), which are to be repealed, have never been used.[144] However, in 2018 the Baniyala
community of Blue Mud Bay in Arnhem Land signed an agreement with the Northern
Territory Government committing to use these provisions to gain increased local
self-government and autonomy.[145]
In 2019 the Department of the Prime Minister and Cabinet informed the Joint
Standing Committee on Northern Australia that the Australian Government had
provided more than a million dollars ($1,075,000) to the Baniyala Nimbarrki
Land Authority (BNLA), a CATSI corporation representing Baniyala, to support
the delegation project.[146]
The proposed repeal would make any future delegation to the BNLA impossible,
and the Explanatory Memorandum states that any existing delegations, or
applications for delegation, will cease on commencement.[147] No information could be
located on whether the BNLA has been consulted on these amendments, or has
agreed to discontinue its request for delegated powers.
Part 4 of Schedule 3 contains amendments with a
delayed commencement. Most notably item 44 amends subsection 70(1) of
the Act to increase the penalty for entering or remaining on Aboriginal land
from 10 penalty units to 50 penalty units. This represents an increase from
$2,220 to $11,100.[148]
There will be a 12-month period from Royal Assent for this change to come into
force.
Schedule 4
Schedule 4 aligns the statutory requirements for payments
into and out of the ABA with current practice and updates the statutory
description of the ABA to place a clear ‘purpose’ of the account within the
legislation. This reflects that payments are currently made based on estimates
of mining royalties rather than final figures, meaning that overpayments may
need to be recouped (or underpayments supplemented) when final figures become
available. As matters stand, the Act only appropriates the consolidated revenue
fund (CRF) for the actual amount of mining revenues rather than for estimates,
meaning that if a payment based upon an estimate turns out to have been an
overpayment, the CRF has been drawn on without a legislated appropriation, in a
technical breach of section 83 of the Constitution. The most recent
annual report for the NIAA states:
Total ABA cash expenditure for 2019-20 is $233.544 million
(2018-19: $206.512 million). Within the 2019-20 expenditure there are four
section 64(3) ALRA payments totalling $0.177 million (2018-19: three payments
totalling $1.66 million) that have technically contravened section 83 of the
Constitution due to difficulties in precisely estimating mining royalties.
Payments out of the ABA are required to be made based on royalties received by
the Northern Territory or Australian Governments. The contraventions occurred
when the royalties upon which the payments were based had been estimated at a
value greater than the eventual actual value. Legislation has been prepared and
is awaiting presentation to Parliament to reduce the non-compliance risks
associated with these payments to an acceptably low level.[149]
This Bill incorporates that legislative proposal. Items
4-7 of this Schedule amend the procedures for appropriation from the CRF so
as to remove the breach.